In light of last month’s cyberattack that originated in and quickly spread ransomware across several countries including the United States, you may be wondering – what exactly is ransomware, what’s the likelihood you’ll be affected, and how can it be prevented?
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is an increasingly popular form of malicious cryptography that infiltrates computer systems, encrypts as much data as possible, and keeps it as a hostage until the victim pays the demanded ransom for the decryption password. The ransom is most often demanded in the form of a digital currency known as “Bitcoin.”
How does it spread?
The attack typically manifests through email phishing campaigns. Once the victim clicks on the link or opens the attachment, the computer becomes infected, encrypting or “locking” the victim out of their files. According to Malwarebytes, roughly 60% of malware payloads in Q1 2017 were ransomware. Other forms of ransomware, however, can travel between computers without user interaction. The “WannaCry” attack being a prime example.
NotPetya, the name given to the ransomware strain first detected in Ukraine, affected computers by using vulnerabilities in the NSA hacking tool known as EternalBlue. By entering Windows-operated machines with unpatched security, the malicious software stole passwords in an attempt to gain administrator access over the entire network. Forced updates then led to mass infection and the encryption of hard drives. It’s worthwhile to note, however, that researchers and academics are now saying the attack was most likely engineered to damage IT systems rather than extort funds.
Who does it affect?
Ransomware affects individuals, as well as companies and organizations – big and small. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, they predict the cost of ransomware damage this year to exceed $5 billion, up from $325 million in 2015.
Since the majority of ransomware occurs through phishing email attacks, perpetrators count on three things:
- Action – you’ll click on the link or download the attachment (either out of curiosity or unintentionally). One wrong click is all it takes
- Poor cyber hygiene – lack of measures including email authentication, intrusion prevention software, and web browser protection.
- Lack of backups – failure to regularly and routinely backup data, especially business-critical data or highly sensitive personal/customer oriented data.
What can I do?
- Backup, backup, backup. Ensure you don’t lose valuable data (and potentially customers) by having to choose between satisfying the demands of your attackers or losing your data forever…or in some cases – both. You can back up critical data using a service such as GoodSync Connect File Transfer Protocol (GSTP) which allows for your backup to go over an encrypted secure channel that ransomware attacks cannot infect, ensuring your backups are secure from even the most advanced ransomware of today. Remember to make sure your mission-critical data is always backed up outside of the ransomware proven infection range. Do not rely on the system security to prevent these attacks; we all seen those fail time and time again. Modern data backup strategy must be flexible enough to mitigate all risks listed below. Such a strategy must include multiple copies of mission-critical data made on geographically dispersed storage mediums, as well as a variety of automation options to match the specifics of each given destination. Below is a table which summarizes suggested backup strategies based on the most likely causes of data loss in today’s dynamic environment.
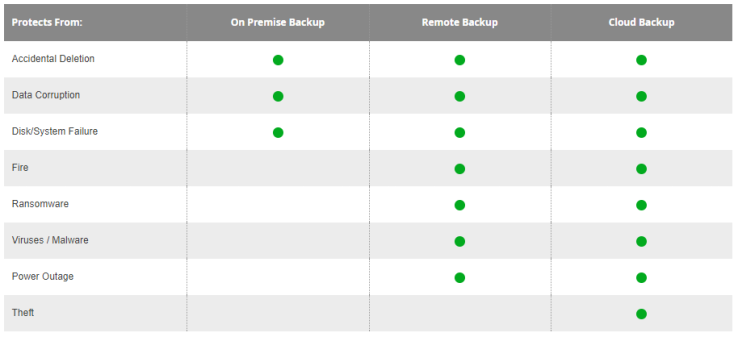
- Establish a business continuity plan in an effort to successfully recognize, advert, and minimize risks.
- Ensure your security software is up-to-date. Click here to see PC Magazine’s top 2017 recommendations.
- Educate yourself, your employees, and your colleagues on safe online practices. With the increase of BYOD work environments, it’s important to mitigate risk through clear policies and protocols, particularly when it comes to the creation and use of passwords. Password Managers such as RoboForm help remove the burden and greatly increase security for both individuals and businesses.
Regardless of motive, ransomware is a real and active threat and it does not discriminate. As 2017 progresses, ransomware will undoubtedly evolve, presenting new variants and tactics. Whether as an individual, business, or organization, ensure you’re taking the proper precautions, removing the incentive for cybercriminals and mitigating losses. And remember, GoodSync allows businesses to completely customize a backup strategy for each given environment by combining the world’s most advanced data backup options with the variety of backup destinations in an easy to use interface. By combining multiple data backup destination options with flexible automation modes, GoodSync can mitigate the entire spectrum of data loss threats, including ransomware.